So, what is a fungal infection? This is a disease caused by fungi, the number of which in nature is very large. Today there are more than 200 species of different mushrooms. Where do fungi live and how does a person get infected?
Fungi are widespread in the environment. They live in the soil, on plants, on animals, and there is also a species of saprophytic fungi that happily coexists with us, i. e. they live on human skin. Human pathogenic fungi that affect the skin are called dermatophytes, and the diseases are called dermatomycosis.
Infection can occur in 2 ways: direct infection through contact with soil, plants, a sick animal or a sick person; indirect - in contact with various things and objects used by patients, including through pet care articles.
Why does fungal infection occur?
Susceptibility to fungal infections is determined by numerous factors: weather conditions (hot season), state of the immune system, skin condition and presence of concomitant diseases. Age, gender and professional factors also matter. More often, obviously, the manifestation of the disease occurs in the hot season, upon returning from the seas, where a hot and humid climate prevails, accompanied by increased sweating.
These factors are particularly favorable for the introduction of pathogenic fungi and the transition of saprophytes into the pathogenic flora.
What are the types of fungal infections?
There are mainly 4 groups of fungal diseases:
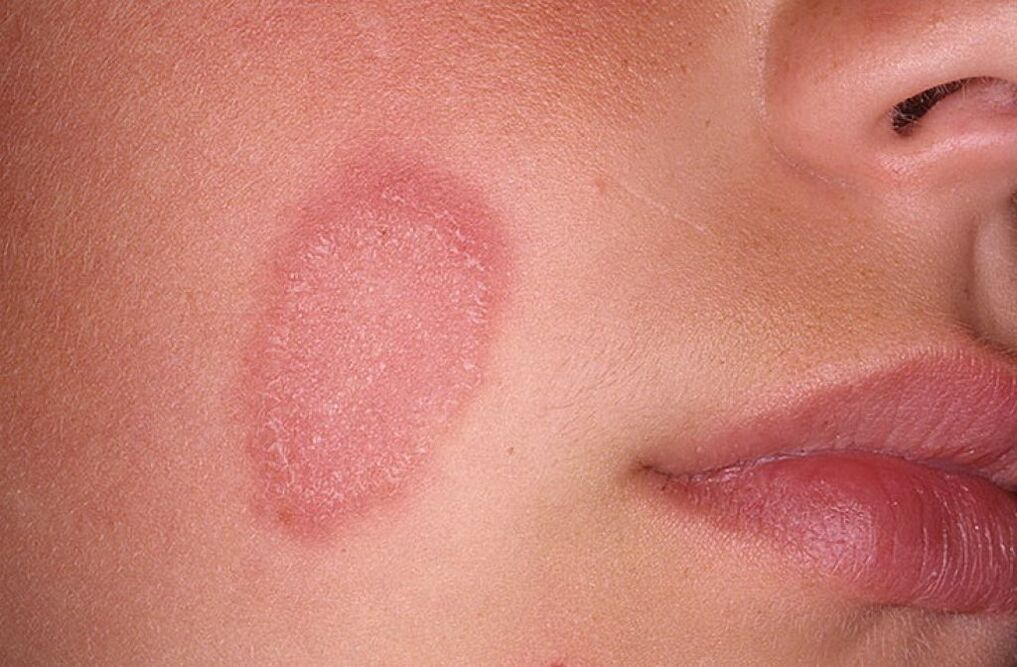
They are rather superficial, as they affect the stratum corneum and hair cuticles, without causing inflammatory reactions and do not affect the skin appendages (hair, nails). The most common disease of this group is pityriasis versicolor or pityriasis versicolor. It manifests itself with the appearance of café-au-lait spots, mainly on the chest, back and shoulder girdle.
This is a large group of fungal diseases that affect the skin, hair and nails. The most common disease of this group is athlete's foot or mycosis of the feet. The disease is very common among the adult population: about 80% suffer from this disease.
A huge role in the prevention of fungal diseases is played by the treatment of shoes, the treatment of manicure and pedicure scissors with special antifungal agents, in the form of solutions and sprays.
It is also important to combat excessive sweating of the skin of the feet, if necessary. For treatment, depending on the severity.
The course and extent of the process use local and systemic antifungal therapy.
In recent years, a modern method has been successfully used in the treatment of fungal nail diseases (onychomycosis) - laser treatment of onychomycosis.
Prevention of fungal diseases
Fungal diseases, also known as mycoses, are infectious diseases caused by pathogenic fungi.
Fungal infections can affect a wide variety of organs. In this case the symptoms can be very different, depending on the affected organ and the type of fungus. There are many types of fungal infections, but forms that affect the skin and nails are the most common. Mycoses are contagious diseases and are transmitted from person to person.
Fungal diseases can appear on any part of the human body: on the torso, limbs, scalp, palms, soles, between fingers, groin and even on the face.
If a fungal disease is detected in a family member, all family members should be carefully checked and, if it is a child, also those who care for the sick child. It is also necessary to carefully check for fungal diseases in children entering orphanages, nurseries, schools and similar institutions.
It is especially important to examine schoolchildren before leaving and after arriving from summer camps.
If you suspect the presence of mycosis, you should consult a dermatologist and get tested for fungus. Before the consultation it is better to cut your hair short, this makes it much easier to recognize mycosis.
At the slightest suspicion of a fungal disease in a child, he should be prohibited from attending school or kindergarten. Immediately after confirmation of the diagnosis it is necessary to start treatment; under no circumstances should the patient be allowed to come into contact with healthy children.
Any object touched by the patient can be contaminated and pose the risk of transmitting the infection or reinfection to the patient himself. Each of these items must be disinfected or destroyed. Clothing is disinfected in a formalin or steam-air vapor chamber. Bedding is disinfected by boiling for 20 minutes.
Prevention of fungal diseases in hairdressing salons, baths and showers should be carried out regularly, at intervals of no more than 3 months. Metallic objects should be thoroughly disinfected with dry heat, the rest in vapor formalin chambers.
Prevention of fungal diseases in animals is of great importance, since very often people are infected with ringworm and microsporia from animals.
It is necessary to create sanitary enclosures and veterinary inspection services on collective farms.
People who have been in contact with sick animals are advised to observe hygiene rules and monitor the condition of their skin, as they can become a source of further spread of the infection, both between people and animals.
Cats and dogs can be carriers of downy microsporum, which is the source of microsporia disease. Animals suspected of carrying a fungal infection should be transferred to special veterinary institutions, but should never be simply removed as they could spread the infection. But there are also known cases where the carriers were rats and mice.
Preventive measures are needed to reduce the possibility of infection of healthy people, so as not to turn them into carriers of a fungal infection. Systematic disinfection of premises is one of the most important points in the prevention process. It is carried out with a 5% chloramine solution, then everything is washed with a 5% soap solution.
Fungal skin lesions
Fungal skin infections are quite common diseases. It can affect any part of the body. To avoid diseases, sanitary and hygienic rules must be observed. Fungal treatment is a complex process, so do not delay your visit to the doctor.
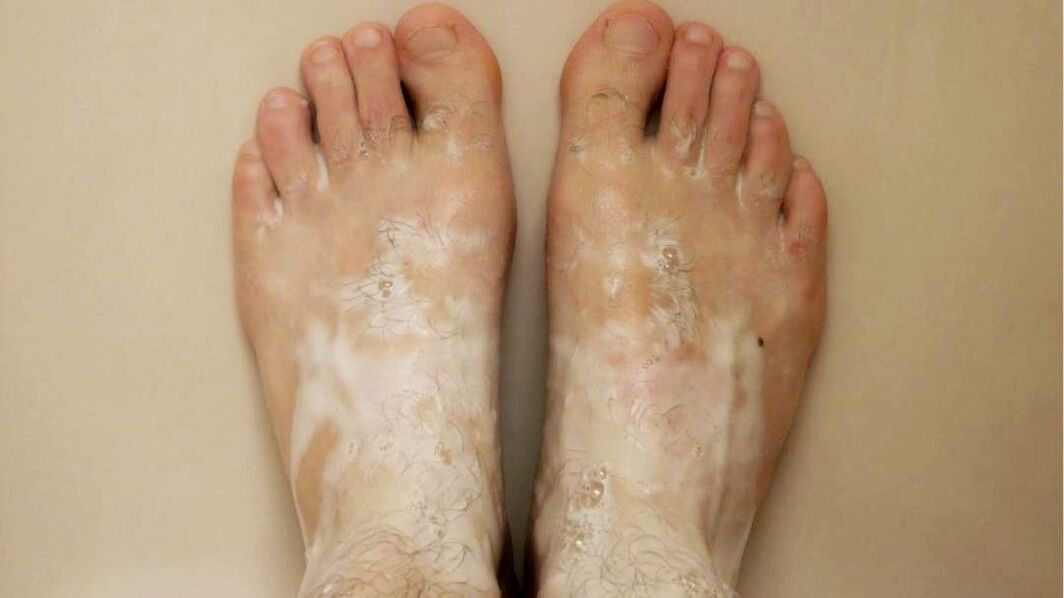
Preparations for the prevention of foot fungus
Foot fungus is an infectious disease that is accompanied by the appearance of blisters, peeling, itching, cracking, etc. To prevent the disease, it is necessary to maintain foot hygiene and use antifungal drugs.
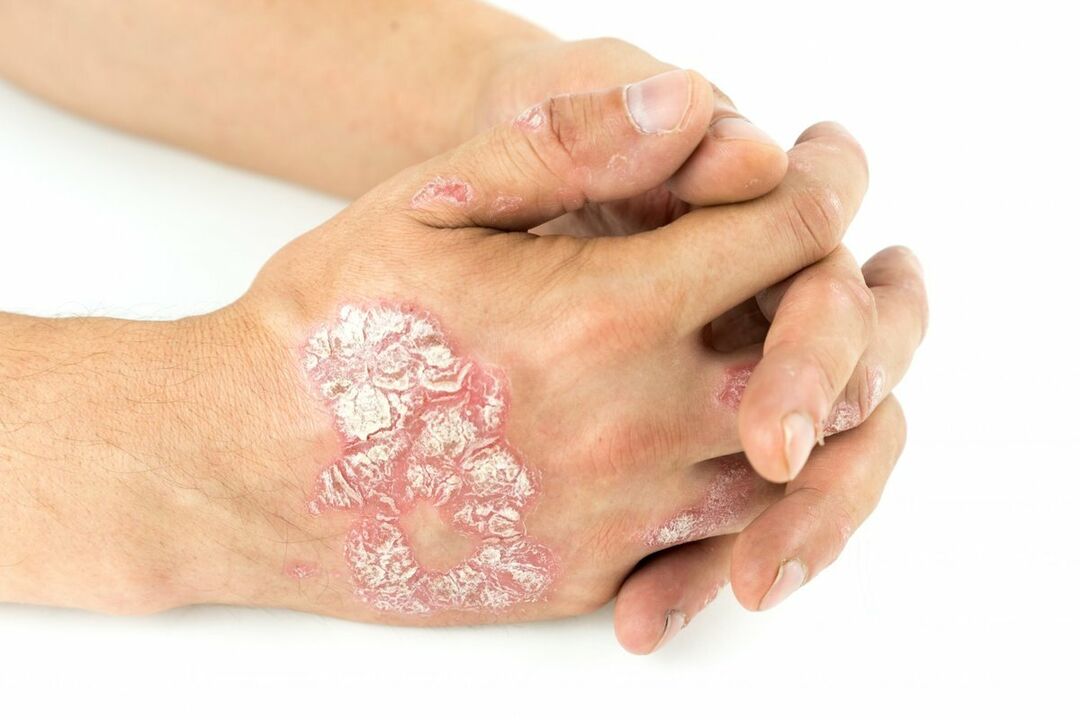
Skin fungus treatment
Skin fungi, or mycosis, often occur in people with weakened immune systems. Affecting the skin, the disease often becomes chronic, reducing the body's ability to resist. There are different types of mycosis, treatment must be carried out individually.

Fungal diseases of the male genital organs
A separate type of male diseases are fungal diseases of the male genital organs, characterized by specific transmission, exclusively through sexual contact. Therefore, it is extremely important to be attentive to your health and carry out preventive activities.
Prevention of fungal diseases. Methods for primary prevention of mycosis
To prevent infection with a pathogenic fungus, several rules must be followed:
- Maintain personal hygiene. Any contact in public places should end with hand sanitisation. To do this, just wash your hands thoroughly or apply an antiseptic solution.
- Public places should be visited with caution. Saunas, toilets, showers and baths are a "fertile ground" for the proliferation of pathogenic microflora. Avoid contact with surfaces in these areas.
- Avoid contact with infected people or animals. This also applies to objects used by patients.
The first sensations of discomfort on the skin or its appendages should not be ignored. It is best to consult a specialist who will determine the cause and be able to prescribe the correct treatment.
Causes of development of mycosis of the feet
Mycosis of the feet is a skin lesion caused by parasitic fungi. A very widespread disease among the population. The surface of the foot and its back, the interdigital space and the nails are involved.
The causative agent is the Trichophyton fungus, which has two varieties. The first is red trichophyton, the second is interdigital. The last type is the most common. According to WHO, up to 30% of residents in developed countries suffer from dermatomycosis of the skin of the foot. This is associated with the constant wearing of shoes, as a result of which the most favorable conditions are created for the development of foot fungi.
Causes of mycosis
The infection is transmitted mainly by contact, through personal items and household items. Horny particles of the skin, contaminated with spores of pathogenic strains of fungi, are a direct source of infection for others.
Microorganisms multiply more intensively in a humid environment. Walking barefoot in public places - bathrooms, saunas, showers - creates the prerequisites for mycosis infection.
Getting into microcracks, abrasions and diaper rash on human skin, spores grow into the thread-like body of the fungus - mycelium. It penetrates deep into the epidermis creating lesions.
The causes of the development of mycosis are:
- reduced immunity due to chronic diseases;
- diabetes;
- varicose veins, thrombophlebitis;
- aged over 60.
These factors reduce the protective functions of the skin, opening access to the penetration of pathogens. At risk are metallurgists, miners, military personnel and athletes, anyone who, for work reasons or working conditions, is forced to constantly wear shoes resistant to water and steam.
Intrafamilial mycoses of the feet are common. Proximity to an infected family member is the shortest route of transmission of a harmful fungal disease.

Symptoms of a fungal infection
Fungal diseases of the feet are manifested by various signs of skin destruction. Depending on the nature of the skin damage, forms of mycosis are distinguished:
- Deleted. The surface of the foot peels, a diaper rash appears between the toes. The itching is mild. Patients often do not attach any importance to this, considering the symptoms of the fungus as an irritation or use ineffective home treatment methods.
- Squamous-hyperkeratic. This shape is also called "moccasin foot" due to the rough and thick leather of the sole, covered in cracks. The damage to the skin is significant: it peels off on a large scale, its color is gray-yellow. There is pain when walking, an unpleasant odor. The disease affects older people more often.
- Wet (vesicular, dehydrotic). Its peculiarity is the formation of small pink bubbles, which over time merge into large bubbles. The disease begins with the arch of the foot, then spreads to the entire foot and toes. When the bubbles burst, they form erosion hotbeds. The skin swells and itches.
- Intertriginous. Characterized by damage to the interdigital space. The skin becomes loose, wet and swollen. Severe itching and burning appear. Over time, deep, painful cracks form and interfere with normal walking.
- Spicy. Severe form of mycosis. It is characterized by fever, inflammation of the inguinal lymph nodes, swelling of the feet and legs. The feet become covered with blisters containing serous-purulent contents. After opening them, oozing erosions form which cause serious physical suffering to the patient.
Pathogenic fungi, feeding on the cells of the human body, release toxins that poison the body. The protective function of the skin and general immunity decrease. Lesions are open doors for bacterial and viral infections. Fungal treatment is a necessary condition for maintaining health and normal well-being.
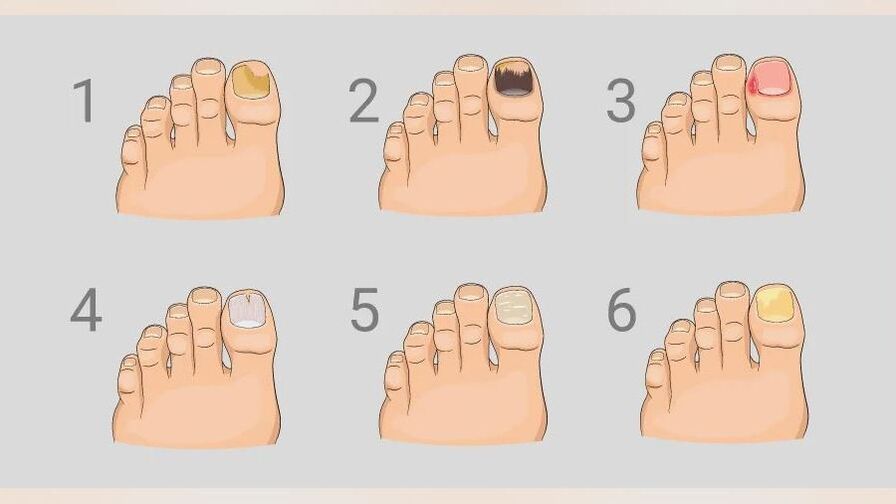
Diagnosis of foot mycosis
Diagnosis and treatment of fungal diseases of the feet are carried out by a dermatologist and mycologist. Determination of the type of fungus is carried out by laboratory methods - studying tissue samples under a microscope. One cultural method for determining the type of pathogen is to place the inoculated material in a nutrient medium. At the same time, the causes of mycosis are determined. Conduct tests for HIV, blood sugar levels, sexually transmitted diseases.
Based on the results obtained, the doctor formulates a diagnosis and prescribes treatment. This can be monotherapy or complex treatments with external agents and tablets.
How to treat athlete's foot
Ringworm treatment is successful when the patient takes medications and procedures responsibly. Modern drugs have a favorable effect on the liver and effectively destroy the mycelium of pathological forms of the fungus.
For wet forms of the fungus, the wounds are first dried using a solution of potassium permanganate, brilliant green, iodine or boric acid. In the treatment of this type of mycosis, drugs containing corticosteroids are essential. The "moccasin foot" is cleaned of keratinized layers by wrapping with salicylic acid. They soften rough skin, which is easy to clean after the procedure.
Treatment with folk remedies for foot fungus
Homemade formulations in the form of:
- foot baths;
- ointments;
- lotions;
- compresses.
- decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs.
The baths last 15-20 minutes. The solution is prepared with the addition of acids: acetic, boric or a mixture of salt and soda. They soften the stratum corneum well. After the procedure, dry the foot and lubricate it with birch tar. After an hour and a half, remove the remaining drug with a napkin. Course – 3 to 5 times. Onions and garlic in the form of compresses disinfect the surface of the feet well. Used in mixture with oils. For minor skin lesions, a decoction of oak bark, juices of celandine, lemon and essential oils of tea tree or fir are effective.
Important. Folk remedies have no contraindications, but their use is most effective in combination with drug treatment.

Consequences of foot mycosis
Like any infectious disease, tinea pedis affects the cells of the human body. Penetrating into the thickness of the skin and feeding on its components, the mycelium grows in the epithelial layers. This does not go unnoticed by the body. Local and general immunity decreases. Allergic reactions may occur and asthmatic manifestations may intensify. Bacterial and viral infections penetrate open wounds. Fungal infections can be accompanied by more serious illnesses.
Important. Mycosis of the feet creates a danger both for the carrier of the dermatophyte and for his immediate environment. People with poor health are more susceptible to contracting fungal diseases. It is necessary to treat the fungus to protect yourself and others.
Prevention of foot fungus
The main preventive measures should be aimed at:
- avoid contact with possible sources of fungal infection;
- maintain personal hygiene;
- maintain a healthy lifestyle;
- treatment of chronic diseases.
If signs of foot mycosis appear, it is necessary to consult a specialist doctor and carry out the prescribed treatment. If preventive measures are taken, cases of recurrence of a fungal disease of the skin of the legs are quite rare.
Fungal infection in the body: symptoms and treatment
The human body is inhabited by many viruses, fungi and bacteria. All of these microorganisms can be beneficial, opportunistic or pathogenic. Furthermore, the latter two types do not cause harm as long as a certain balance is maintained between the microorganisms
Fungal infection
The human body is inhabited by many viruses, fungi and bacteria. All of these microorganisms can be beneficial, opportunistic or pathogenic. Furthermore, the latter two types do not cause harm as long as a certain balance is maintained between the microorganisms.
The greatest danger is posed by a fungus, a microorganism that can cause damage to a person's skin and internal organs. There are approximately 500 species of fungi that cause mycosis in humans. What fungal infections can cause serious diseases in people, and what treatment methods are used to eliminate pathogenic microorganisms?

Types of mushrooms
All fungi that can live in the human body are divided into several types:
- yeast;
- moldy;
- domiphoric.
Fungi are multicellular
Yeasts live in the human body, being part of its microflora. They belong to opportunistic species, as they do not pose a health risk, provided that balance is maintained. All other types of fungi are pathogenic and pose a real threat to human health and life.
Fungi can multiply both on the surface of the skin and nails, and inside the body. However, a healthy person, as a rule, is not affected by a fungal infection, as it is destroyed by the cells of the immune system. Therefore, in the body of people with weakened immunity, the most favorable conditions are created for the functioning of the fungus.
Characteristics of cutaneous mycosis
The skin very often suffers from fungal infections. Furthermore, it spares neither women, nor men, nor children. This disease is divided into several main groups:
- athlete's foot;
- dermatomycosis;
- sporotrichosis;
- candidiasis;
- trichophytosis.
Athlete's foot is a fungal disease caused by fungi of the genus Epidermophyton. It affects men more often. With athlete's foot, not only the top layer of skin is affected, but also the nails.
There are two forms of this disease:
- athlete's foot inguinal;
- athlete's foot.
Dermatomycoses are a whole group of fungal skin infections that affect one in five people on the planet. In this case, mycosis can develop not only on the skin, but also in the internal organs.
Sporotrichosis is a chronic fungal disease caused by fungi of the Sporotrichium genus. Infection occurs through contact with grass, shrubs, soil, road dust and even food. In this case, the skin and subcutaneous tissue are often affected. Mucous membranes and internal organs are very rarely exposed to the fungus.
Candidiasis is caused by yeast fungi of the Candida genus. These microorganisms are part of the healthy microflora and perform important functions in the human body. However, when favorable conditions are created, Candida fungi begin to actively multiply, disturbing the balance of bacteria, which leads to the development of candidiasis. Most often, candidiasis or thrush appears in the vagina of women and in the mouth of children.
Causes of fungal infection
The development of a fungal infection is facilitated by contact with a source of fungi. For example, their spores can be found in the air, on the floor or in bird droppings. At the same time, to reproduce, fungi need a special environment, which is created when the protective functions of the organism are reduced.
While athlete's foot can affect anyone, there are certain populations that are more susceptible to developing the disease.
These include:
- people who have undergone organ transplant operations;
- cancer patients, as well as people undergoing chemotherapy and radiotherapy;
- people with diabetes and lung diseases.
Fungi can grow on the surface of the skin. But the favorite places for dislocation are the folds of the skin, the folds of the arms and legs, that is, all places where there is high humidity and body temperature. Mycosis can spread to a small area, such as between the fingers or toes. But some fungi are capable of infecting deep layers of tissues. If mycosis develops in the lungs, it enters the bloodstream, causing damage to internal organs.
Coccidioidomycosis
This disease is caused by fungi of the genus Coccidioides imitus, which live in the soil. This microorganism is common in the driest areas of America, Africa and Mexico. It enters other countries along with the goods supplied by these countries.
Signs of coccidioidomycosis
The first symptoms of the disease resemble ARVI and inflammatory processes in the lungs and bronchi. The presence of fungi is indicated by the following signs:
- slight increase in body temperature;
- chills;
- heachache;
- feeling tired;
- general weakness of the body.
Subsequently, chest pain, shortness of breath and dry cough are added to these symptoms. A couple of weeks after the pulmonary manifestations of the disease, the patient develops skin rashes in the form of papules or nodules that look like warts.
Histoplasmosis
This disease is caused by the fungus Histoplasma capsulatum, which most often affects the lungs. In some cases, the fungus spreads to other organs and, if left untreated, leads to the patient's death. People with AIDS are susceptible to this disease due to the vulnerability of their immune system.
Signs of histoplasmosis
The acute form of the disease is often asymptomatic, which complicates the diagnosis and delays the start of treatment. In severe cases, patients experience the following symptoms:
- increase in body temperature up to 40°-41°C
- chills followed by heavy sweating;
- severe headaches and muscle pain;
- chest pain;
- dry cough;
- general weakness.
If left untreated, the disease becomes chronic.
Features of the treatment of fungal infection
Treatment of any fungal infection involves internal administration of antifungal drugs, as well as symptomatic therapy to improve the general condition of the patient. In severe forms of the disease, drugs are administered intravenously. The duration of treatment depends on the type of fungal infection and the severity of the disease. Typically ranges from 1 to 3 months. In addition, patients are prescribed drugs that strengthen the body's immune system.
Preventive actions
The fungus is an insidious microorganism that is difficult to destroy. Therefore, any infection is easier to prevent. First of all, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system, which will allow it to independently fight any pathogens.
It is also recommended to follow the following rules:
- maintain personal hygiene, wash your hands before eating, after each visit to the bathroom and public places;
- wash fruit and vegetables carefully;
- animal feed must be subjected to prolonged heat treatment;
- eat rationally, minimizing the consumption of simple carbohydrates and sugars;
- monitor body weight;
- take antibacterial and hormonal drugs only as prescribed by a doctor;
- use a condom during sexual intercourse.
It is very important, if you find several signs of a fungal infection, to consult a doctor and undergo a complete body examination.
Modern dermatology has a number of antifungal drugs that are harmful to fungi and non-toxic to the human body. They exist in various dosage forms: for local and systemic use.
























